ஜீன்
ஜீன் என்பது, ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட மரபு பண்பை வைத்திருக்கும் பெட்டகம் எனலாம். இவை, DNA-யில் காணப்படும் நுண் துண்டங்கள். உதாரணமாக, ஒரு மீனின் நிறத்திற்கான மரபு பொருளை ஒரு ஜீன் வைத்திருக்கலாம். மற்றொரு ஜீனோ, அதன் துடுப்பு எவ்வளவு நீளம் இருக்கவேண்டும் என்பதற்கான மரபு பொருளை வைத்திருக்கலாம். Genes are segments of DNA that contain instructions for building and maintaining an organism. In a fish, one gene might carry the instructions for producing the pigment responsible for the fish's coloration, while another gene might provide instructions for the development of its gills.
ஜீனோம்
எல்லா ஜீன்களையும் சேர்த்து ஜீனோம் என்பது வழமை. A genome is the complete set of an organism's genetic material, which includes all of its genes.
அல்லீல்
ஒரு ஜீன், மீனின் வால் சற்று நீளமானதாகயிருக்கும் வண்ணம் மரபுபொருளை வைத்திருக்கும். மற்றொன்றோ, கட்டையாகயிருப்பதற்கான மரபுபொருளைக் கொண்டிருக்கும். இரண்டும் மீன் வாலின் நீளத்திற்கான மரபுபொருளை வைத்திருந்தும், ஒன்றுக்கொன்று மாறுபடுகின்றன. அதாவது, ரகம் ரகமாக (Versions) உள்ளன. இவற்றையே, அல்லீல்கள் என்பர்.Alleles are different versions or variants of a gene. Let's say there's a gene in a fish that determines its fin shape. There might be two alleles of this gene: one that results in a fish having long, pointed fins and another that results in short, rounded fins. These are two different alleles of the same gene that lead to variations in the fish's fin shape.
ஹோமோலாகஸ் குரோமோசோம்கள்
ஹோமோலாகஸ் குரோமோசோம்கள் எனப்படுபவை ஒரே வகை ஜீன்களின் வெவ்வேறு அல்லீல்களைக் கொண்டிருக்கும் குரோமோசோம்கள். Homologous chromosomes are a pair of chromosomes found in diploid organisms, like humans, that carry the same genes but may have different alleles (variants) of those genes. These chromosomes are similar in size, shape, and gene content. One homologous chromosome in the pair comes from the organism's mother, and the other comes from the organism's father.
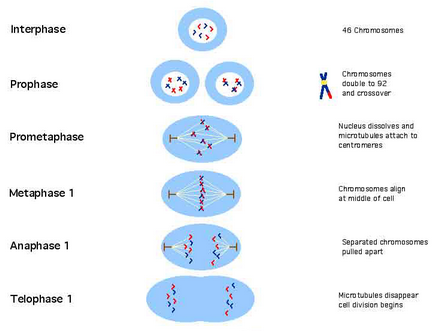
Meiosis I-ன் முதல் நிலை : Prophase I
இந்த நிலையில், உட்கருவினுள், ஹோமோலாகஸ் குரோமோசோம்கள் ஜோடியாகின்றன. அதாவது, ஒரு குரோமோசோம், மீனின் வால் நீளம் கட்டையாகயிருக்கவும், பிரிதொன்று, நீளமானதாகயிருக்கவுமான மரபுபொருளைக் கொண்டிருக்கலாம். அதாவது, அல்லீல்களாகயிருக்கலாம்! இவ்வாறு அல்லீல் ஜோடிகள் உருவாவதை, Synapsis என்பர். இப்படி ஜோடிகள் உருவாகும்போது, அவற்றினுளுள்ள மரபு பொருட்கள் ஒன்றாக கலக்க வாய்ப்புள்ளது. அவ்வாறு கலக்கும் செயலுக்கு, Crossing Over என பெயர். இப்படி கலந்தால், புதிய மரபு பண்புகள் தோன்றும். அதாவது, நெட்டையாகவுமல்லாமல் குட்டையாகவுமல்லாமல் புதிய நீளத்தில் வாலுடைய மீன் தோன்றலாம். கடைசியாக, உட்கரு வெடித்து, உள்ளேயுள்ள ஜோடிகள் செல்லினுள் வலம் வரும். சுரைக்காய் பலூனின் நடுவில் ரப்பர் இடப்பட்ட அமைப்பில்தான் இவையும் இருக்கும். ரப்பர் இடப்பட்ட பகுதி, சென்ட்ரோமியர் எனப்படும். This is the longest and most complex phase of meiosis. During this stage, homologous chromosomes (chromosomes with similar genes but potentially different variants or alleles) pair up in a process called synapsis. This pairing forms structures called tetrads. Genetic recombination, or crossing-over, can occur between chromatids of homologous chromosomes, leading to genetic diversity. At the end of prophase I, the nuclear envelope breaks down.
Meiosis I-ன் இரண்டாம் நிலை : Metaphase I
இந்நிலையில், ஹோமோலாகஸ் குரோமோசோம் ஜோடிகள், மெட்டாஃபேஸ் தட்டு எனப்படும் அமைப்பில் அடுக்கப்படுகின்றன. மைட்டாஸிஸில் இருந்ததுபோலவே, இங்கும் ஸ்பின்டிள் நார்கள்தான் இந்த ஜோடிகளை நட்டநடுவில் கொணர்கின்றன. The tetrads align at the cell's equatorial plane, known as the metaphase plate. Unlike mitosis, where individual chromosomes align, here, homologous chromosomes are paired.
Meiosis I-ன் மூன்றாம் நிலை : Anaphase I
ஜோடிகள் பிரிக்கப்படவேண்டிய நேரம் நெருங்கிவிட்டது. சென்ட்ரோமியரில் கீறல் ஏற்பட, ஜோடிகள் வடகலை, தென்கலை என்பது போல, இரு குழுக்களாக பிரிகின்றன. Homologous chromosomes are pulled apart and move to opposite poles of the cell. Each resulting cell now has a unique combination of genetic material due to crossing-over.
Meiosis I-ன் நான்காம் நிலை : Telophase I
இப்போது, பிரிந்துபோய் தனித்து நிற்கும் ஜோடிகளை உட்கரு கவசம் மூடிடும். சைட்டோகைனெஸிஸ் நிலையில், இந்த இரண்டு கவசஞ்சூழ்ந்த அமைப்புகளும், தனி செல்களாக மாறி வெளிவருகின்றன. இதில், நினைவில் கொள்ளவேண்டியது, குரோமோசோம்களின் எண்ணிக்கையைத்தான். மைட்டாசிஸிலோ, அவை இரட்டிப்பாக்கி பிரிக்கப்பட்டன. எனவே, குழந்தை செல்களிடமும் சம எண்ணிக்கையில் குரோமோசோம்கள் இருந்திருக்கும். ஆனால் மியாசிஸிலோ, ஜோடிகள் அப்படியே பிரிக்கப்படுகின்றன. அப்படியென்றால், குழந்தை செல்களிடம் பாதி எண்ணிக்கையில்தான் குரோமோசோம்கள் காணப்படும். இதை, ஹாப்ளாய்டு என்பர். The cell undergoes cytokinesis, splitting into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell is haploid, meaning it has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. However, each chromosome is still composed of two sister chromatids.
கருத்துகள்