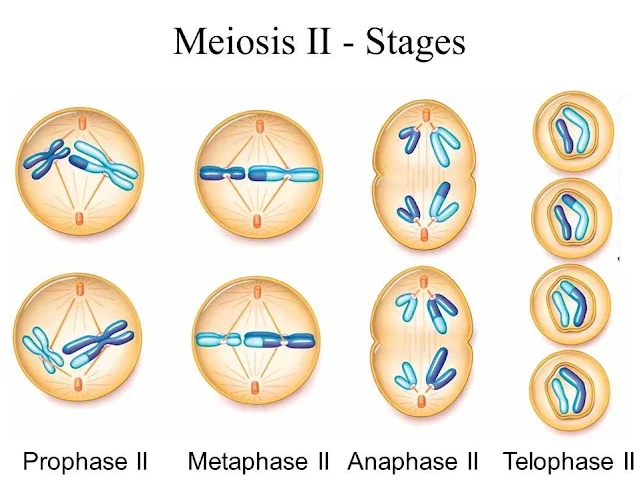
மியாசிஸ் செல் பிரிதலின் இரண்டாம் நிலை : மியாசிஸ் II
ஹேப்ளாய்டு : பொதுவாக ஒரு உயிரினத்தின் உடலில் காணப்படும் குரோமோசோம்களின் எண்ணிக்கையில் பாதியை மட்டுமே கொண்டிருக்கும் செல்கள். மியாசிஸில் உருவாகும் செல்களில், குரோமோசோம் எண்ணிக்கை பாதியாக குறையக்கண்டோம்! அவை, ஹேப்ளாய்டுகள்தான்! Haploid refers to a cell or organism that has a single set of chromosomes (n). In humans, the haploid number is 23. This means that gametes, like sperm and eggs, have 23 chromosomes each. Haploid cells are produced through meiosis, where the chromosome number is reduced by half.
டிப்ளாய்டு : இரட்டைப்படை எண்ணிக்கையில் குரோமோசோம்களை கொண்டிருக்கும் செல்கள். Diploid refers to a cell or organism that has two sets of chromosomes (2n). In humans, the diploid number is 46, as most of our somatic cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs). Diploid cells have two homologous copies of each chromosome, one inherited from each parent.
கேமேட் : இனப்பெருக்க செல்களுக்கு, பொதுவாக கேமேட் என பெயர். இவை, ஹேப்ளாய்டுகள்! மியாசிஸில்தானே உருவாகின்றன?! Gametes are specialized sex cells involved in sexual reproduction. In humans, the two primary types of gametes are sperm (produced by males) and eggs or ova (produced by females). Gametes are haploid, meaning they have half the chromosome number of somatic cells (body cells).
சைக்கோட் : ஹேப்ளாய்டுகளாக இருக்கும் எதிரெதிர் பாலின இனப்பெருக்க செல்கள், ஒன்று சேருகையில் டிப்ளாய்டுகளாகின்றன. இவையே, சைக்கோட்டுகள்! A zygote is a cell formed by the fusion of two gametes during fertilization.It represents the first cell of a new individual in sexually reproducing organisms. The zygote is diploid because it contains one set of chromosomes from each parent, resulting in a complete set of chromosomes (46 in humans).
மியாசிஸ் II-ன் முதல் நிலை : புரோஃபேஸ் II
மியாசிஸ் ஒன்றில், புதிய ஹேப்ளாய்டு செல்கள் உருவானதைக் கண்டோம். இவற்றிலுள்ள குரோமோசோம்கள், ஜோடியான குரோமட்டிடு அமைப்புகளைக் கொண்டிருக்கும் என அறிந்தோம். மேலும், அவை நடுவே சென்ட்ரோமியரில் கட்டப்பட்டுள்ளன என்றும் கண்டோம். புரோஃபேஸ் இரண்டில் புதிதாக உருவான இந்த செல்களின் உட்கருக்கள் வெடித்து, உள்ளேயுள்ள குரோமோசோம்கள், செல்லின் சைட்டோபிளாசத்தில் வலம் வருகின்றன. The cells produced during meiosis I enter prophase II, where the nuclear envelope may break down again, chromosomes condense, and spindle fibers form.
மியாசிஸ் II-ன் இரண்டாம் நிலை : மெட்டாஃபேஸ் II
இதில், வழக்கம்போல குரோமோசோம்கள் செல்லின் நட்டநடுவில் அடுக்கப்படுகின்றன. Chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, similar to metaphase in mitosis. Importantly, each chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids.
மியாசிஸ் II-ன் மூன்றாம் நிலை : அனாஃபேஸ் II
இந்நிலையில், அடுக்கப்பட்ட குரோமோசோம்கள், இரு திசையிலும், ஸ்பின்டிள் நார்களோடு இழுக்கப்படும் என அறிந்துள்ளோம். The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers and move toward opposite poles of the cell.
மியாசிஸ் II-ன் நான்காம் நிலை : டீலோஃபேஸ் II
உட்கரு கவசம், உண்டான குழுக்களை சூழும் நிலை இது! Nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromatids, resulting in the formation of four distinct haploid daughter cells, each with a unique combination of genetic material.
மியாசிஸ் II-ல் என்னதான் நடக்கிறது?
மியாசிஸின் முதல்நிலையில் உருவாகும் இரண்டு புது ஹேப்ளாய்டு செல்களையும், அவற்றின் ஜோடி குரோமட்டிடுகளை மேலும் பகர்த்து, ஒன்றுக்கொன்று மரபுரீதியில் மாறுபடும் நான்கு புது செல்களை உருவாக்குதல். Meiosis II occurs as the second stage of meiosis, a specialized form of cell division that is crucial for the formation of haploid gametes (sperm and egg cells) in sexually reproducing organisms. The primary purpose of meiosis II is to further reduce the chromosome number, ensuring that the resulting gametes are haploid and genetically diverse. Meiosis I, the first stage of meiosis, separates homologous chromosomes, reducing the chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) in two daughter cells. These haploid cells each have one set of chromosomes, but they are still composed of pairs of sister chromatids held together by centromeres. The next step is to separate these sister chromatids, which are genetically identical copies of each chromosome. Meiosis II accomplishes this separation.
கருத்துகள்